Teaching
Welcome to our teaching page! Our focus is on project-based learning that empowers students to actively engage with real-world challenges in digital health and shared decision-making. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, innovative digital formats, and a strong commitment to Open Science and ethical research, we create hands-on, inclusive learning environments. By supporting early-career researchers—especially women—and integrating digital competencies, we prepare the next generation of professionals to shape the future of healthcare.

Theory, tools and methods in biology
lecture, course
HP. Herzel, R. Kempter, S. Schreiber, P. Kuokkanen, R. Steuer, JH. Schleimer, P. Romanczuk, N. Blüthgen, M. König
04/2025 - 09/2025 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
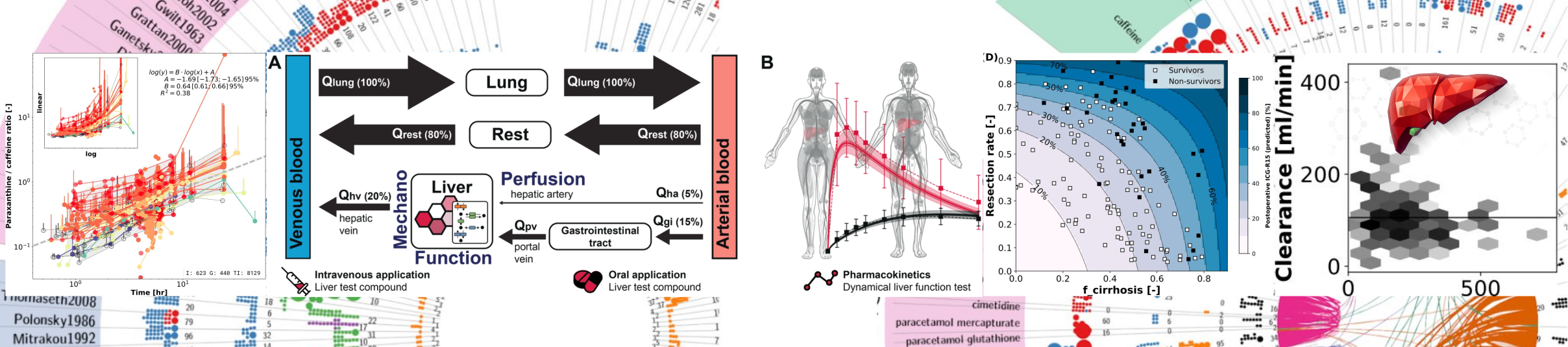
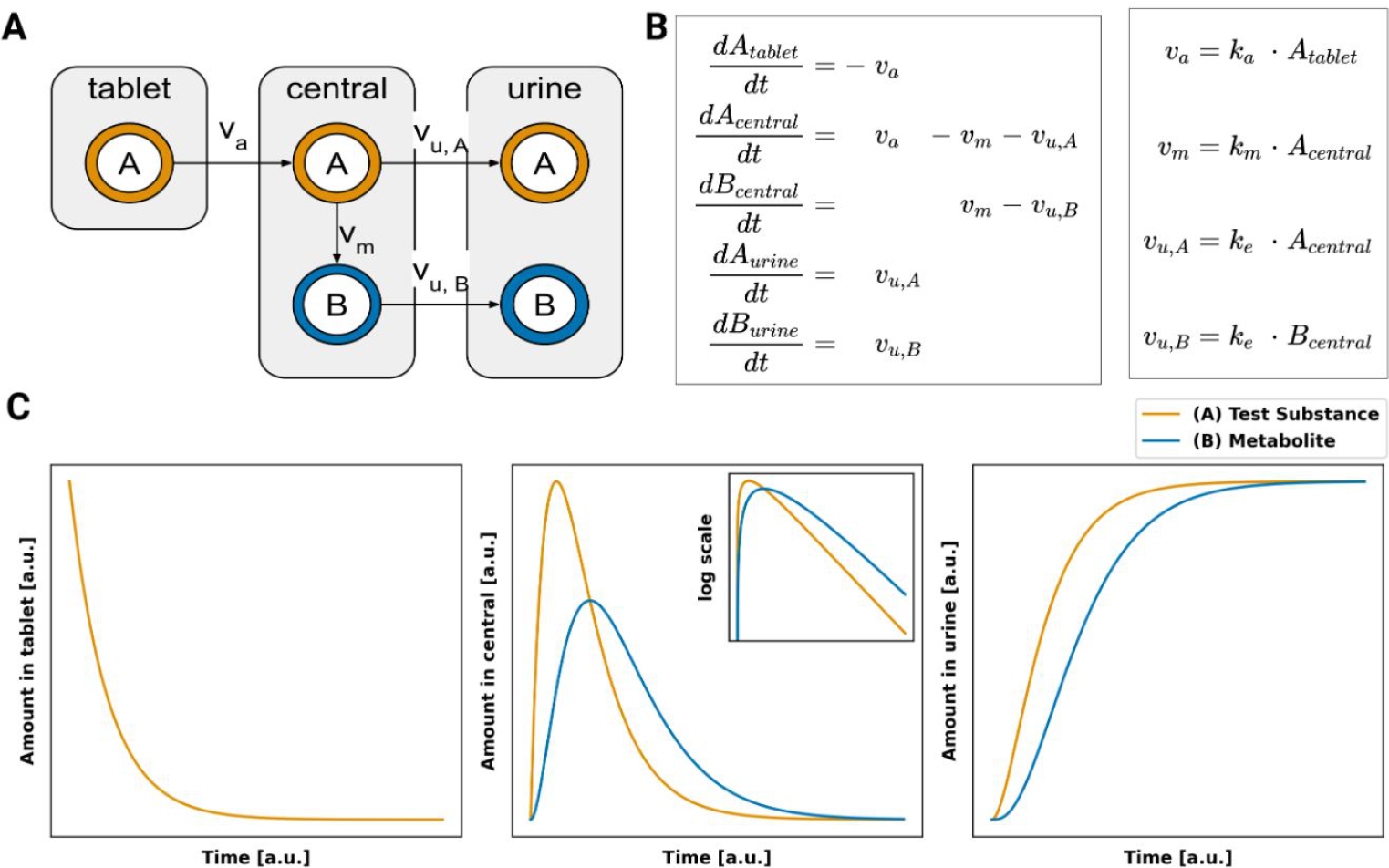
Within this course and lecture important theory, tools and methods in biology are presented. Our group was responsible for the submodule pharmacokinetic modelling with information and material available from https://github.com/matthiaskoenig/course-pharmacokinetic-modelling.
Pharmacokinetic modelling is the study of how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body. The course on pharmacokinetic modelling will cover topics such as pharmacokinetic principles, drug distribution, clearance, and elimination, and the factors that affect these processes. Students will learn about different models used to describe pharmacokinetics, such as compartmental models and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models, and how to use these models to predict drug concentrations and optimize dosing regimens. Other topics that might be covered include pharmacodynamics, drug-drug interactions, and the use of pharmacokinetic modelling in drug development and clinical practice. Overall, a course on pharmacokinetic modelling will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and techniques used to describe the movement of drugs through the body, and how this knowledge can be applied to improve drug therapy.
Theory, tools and methods in biology
lecture, course
HP. Herzel, R. Kempter, S. Schreiber, P. Kuokkanen, R. Steuer, JH. Schleimer, P. Romanczuk, N. Blüthgen, M. König
04/2024 - 09/2024 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
Within this course and lecture important theory, tools and methods in biology are presented. Our group was responsible for the submodule pharmacokinetic modelling with information and material available from https://github.com/matthiaskoenig/course-pharmacokinetic-modelling.
Pharmacokinetic modelling is the study of how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body. The course on pharmacokinetic modelling will cover topics such as pharmacokinetic principles, drug distribution, clearance, and elimination, and the factors that affect these processes. Students will learn about different models used to describe pharmacokinetics, such as compartmental models and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models, and how to use these models to predict drug concentrations and optimize dosing regimens. Other topics that might be covered include pharmacodynamics, drug-drug interactions, and the use of pharmacokinetic modelling in drug development and clinical practice. Overall, a course on pharmacokinetic modelling will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and techniques used to describe the movement of drugs through the body, and how this knowledge can be applied to improve drug therapy.
X-Student Research Group: Physiologically based digital twins for the treatment of hypertension with ACE inhibitors and diuretics
lecture, course
M. König
04/2023 - 09/2023 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Physiologically based digital twins for the treatment of hypertension with ACE inhibitors and diuretics.
Physiologically based digital twins for the treatment of hypertension with ACE inhibitors and diuretics.
Understanding a drugs pharmacokinetics - how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolised and excreted by the body - and its pharmacodynamics - how it affects the body - is a key challenge in treating people. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and diuretics are two classes of drugs used to treat high blood pressure. Both are among the most commonly prescribed drugs due to the high prevalence of hypertension in an ageing society.
In this X-student research group we will develop physiologically based pharmacokinetic models of the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide and the ACE inhibitor lisinopril. The methodological approach is a combination of lectures, tutorials and practical work by the students. The research project is aimed at students with a STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) background, including biology, computer science and medical students. Basic programming skills in Python are required.
With the X-Student Research Groups, the Berlin University Alliance supports research teams consisting of young researchers and students. The goal is to involve students in current research projects of the alliance partners and to enable them to participate in (cutting-edge) research already during their studies.
Funded under the Excellence Strategy of the Federal Government and the Länder by the Berlin University Alliance.
Theory, tools and methods in biology
lecture, course
HP. Herzel, R. Kempter, S. Schreiber, P. Kuokkanen, R. Steuer, JH. Schleimer, P. Romanczuk, N. Blüthgen, M. König
04/2023 - 09/2023 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
Theory, tools and methods in biology - Pharmacokinetic modelling
Within this course and lecture important theory, tools and methods in biology are presented. Our group was responsible for the submodule pharmacokinetic modelling with information and material available from https://github.com/matthiaskoenig/course-pharmacokinetic-modelling.
Pharmacokinetic modelling is the study of how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body. The course on pharmacokinetic modelling will cover topics such as pharmacokinetic principles, drug distribution, clearance, and elimination, and the factors that affect these processes. Students will learn about different models used to describe pharmacokinetics, such as compartmental models and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models, and how to use these models to predict drug concentrations and optimize dosing regimens. Other topics that might be covered include pharmacodynamics, drug-drug interactions, and the use of pharmacokinetic modelling in drug development and clinical practice. Overall, a course on pharmacokinetic modelling will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and techniques used to describe the movement of drugs through the body, and how this knowledge can be applied to improve drug therapy.
X-Student Research Group: Physiologically based modeling of drugs: ACE inhibitors in the treatment of high blood pressure
lecture, course
M. König
10/2022 - 03/2023 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
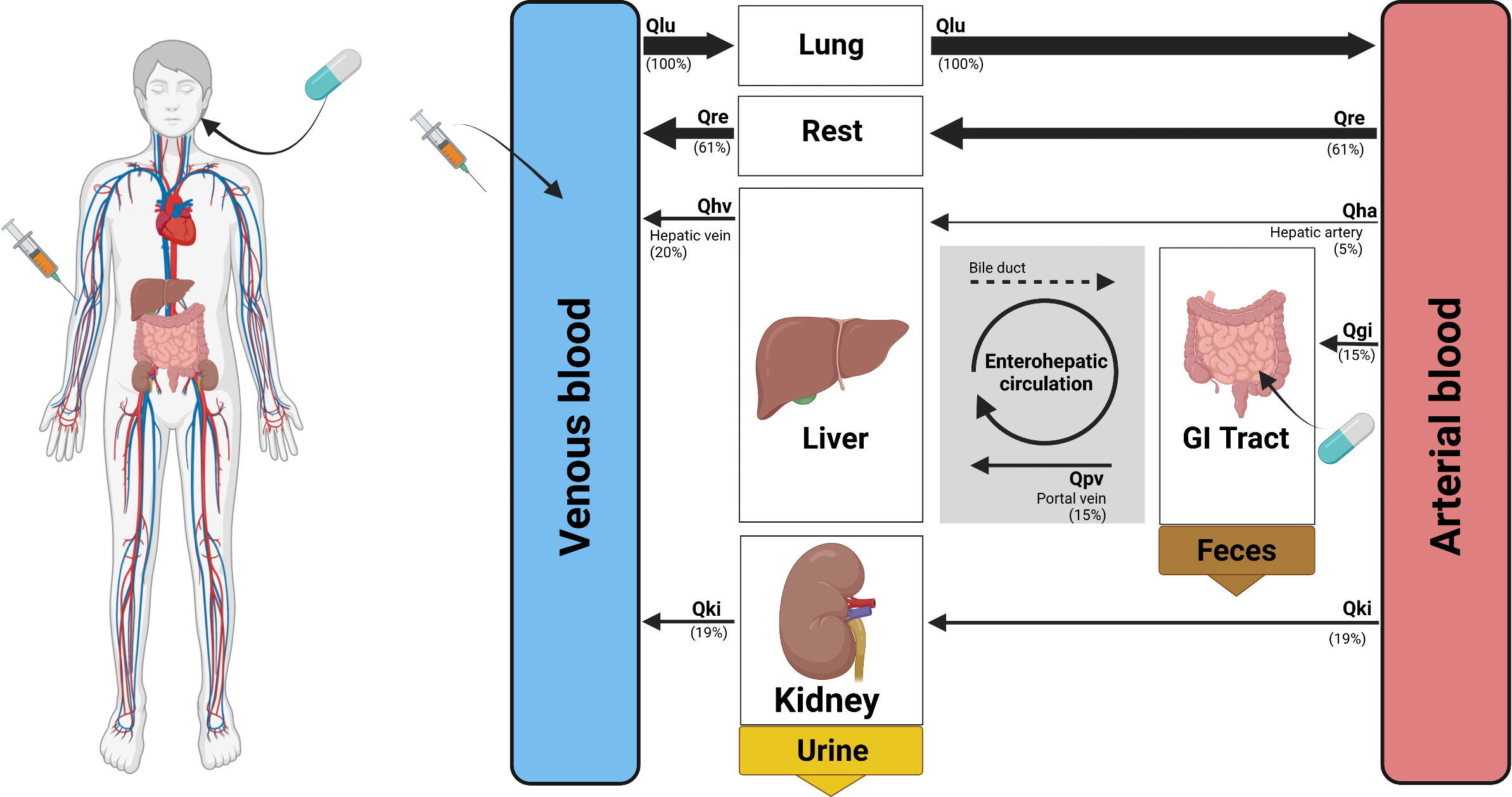 Physiological-based pharmacokinetics model of the ACE inhibitors. The models will study the absorption (GI tract), distribution (systemic circulation), metabolization (liver) and elimination (kidneys and liver) of the ACE inhibitors lisinopril and ramipril. Organs and plasma volumes are connected via the blood flow (Q).
Physiological-based pharmacokinetics model of the ACE inhibitors. The models will study the absorption (GI tract), distribution (systemic circulation), metabolization (liver) and elimination (kidneys and liver) of the ACE inhibitors lisinopril and ramipril. Organs and plasma volumes are connected via the blood flow (Q).
A key challenge in treating people is to understand the pharmacokinetics of a given drug, i.e., how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body, and the pharmacodynamics of the drug, i.e., how the substance is affecting the body. Physiological-based pharmacokinetics (PBPK) models are computational models which allow the study of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs in silico. Within this X-Student Research Group we will develop together with the students PBPK models of ACE inhibitors. The methodical approach is a combination of lectures, tutorials, and practical work by the students. The research project is aimed at a maximum of 15 students primarily for students with STEM (science, technology, engineering, math) background including biological, informatic and medical students. Basic programming skills in Python are required.
With the X-Student Research Groups, the Berlin University Alliance supports research teams consisting of young researchers and students. The goal is to involve students in current research projects of the alliance partners and to enable them to participate in (cutting-edge) research already during their studies.
The Berlin University Alliance supports up to 32 X-Student Research Groups per year.
- X-Student Research Groups
- FAQ X-Student Research Groups
- Additional information X-Student Research Group
Funded under the Excellence Strategy of the Federal Government and the Länder by the Berlin University Alliance.
Important models of quantitative biology from the literature
seminar, course
R. Steuer, P. Romanczuk, N. Blüthgen, M. König
10/2021 - 03/2022 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
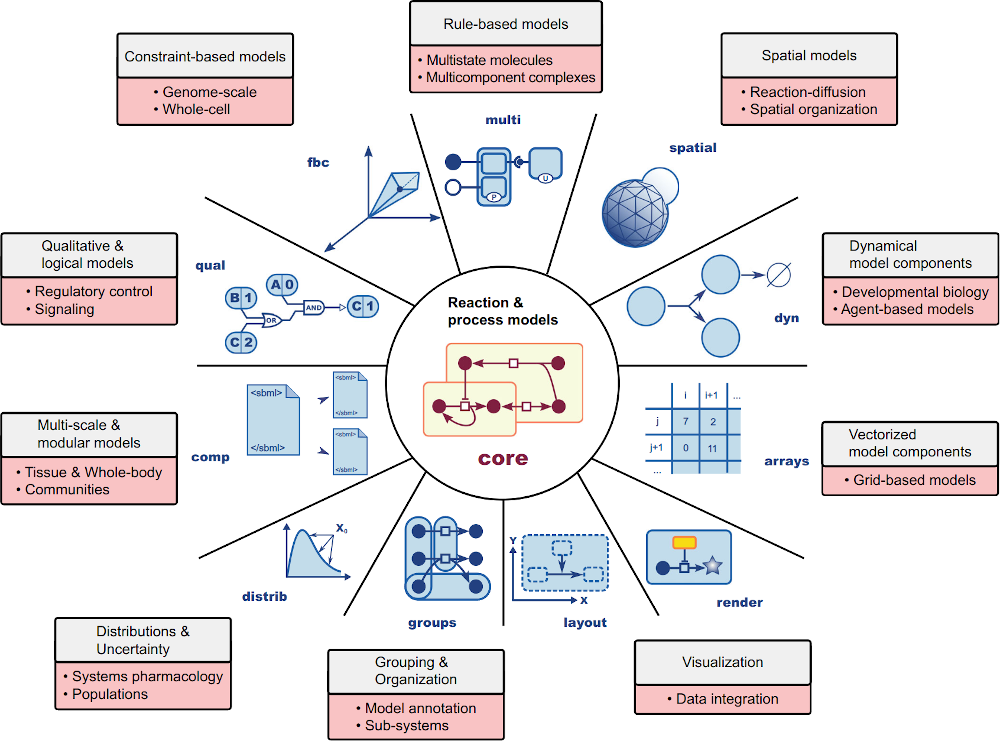 Important models in quantitative biology
Important models in quantitative biology
This course discusses, implements and analyses important models in quantitative biology. The course covers Boolean and ordinary differential equation models from metabolism and signalling.
Important models of quantitative biology from the literature
seminar, course
R. Steuer, P. Romanczuk, N. Blüthgen, M. König
10/2020 - 03/2021 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Important models in quantitative biology
Important models in quantitative biology
This course discusses, implements and analyses important models in quantitative biology. The course covers Boolean and ordinary differential equation models from metabolism and signalling.
Models of cellular processes
lecture
M. König, R. Steuer
10/2019 - 03/2020 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
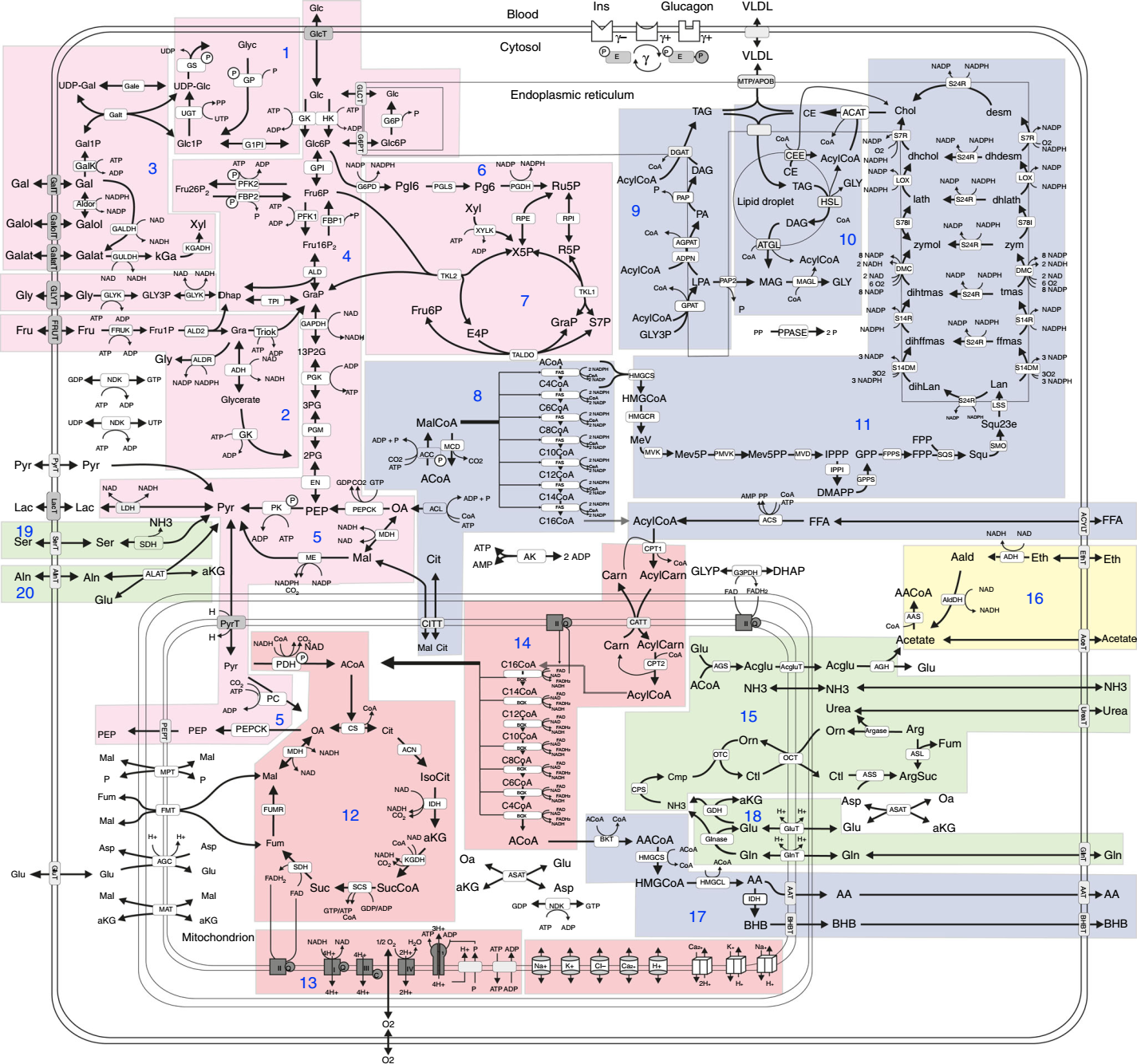 Important models in quantitative biology
Important models in quantitative biology
This course introduces, implements and analyses models of cellular processes. The lecture covers constraint-based models, Boolean models and ordinary differential equation models from metabolism and signalling. Methods such as parameter optimisation, stochastic models and sensitivity analysis are introduced.
Important models of quantitative biology from the literature
seminar, course
N.Blüthgen, M.König, R.Steuer
10/2019 - 03/2020 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Important models in quantitative biology
Important models in quantitative biology
This course discusses, implements and analyses important models in quantitative biology. The course covers Boolean and ordinary differential equation models from metabolism and signalling.
Important models of quantitative biology from the literature
seminar, course
N. Blüthgen, R.Steuer, M. König
10/2018 - 03/2019 - Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Biology, ITB
 Important models in quantitative biology
Important models in quantitative biology
This course discusses, implements and analyses important models in quantitative biology. The course covers Boolean and ordinary differential equation models from metabolism and signalling.